OGD Quality Management
Definition of Open Government Data
According to the ACT ON PROMOTION OF THE PROVISION AND USE OF PUBLIC DATA, ‘open government data' is created or acquired and managed by public institutions and is processed in optical or electronic methods, and codes, characters, figures, colors, voices, sounds, images And any kind of material or information expressed in video (including complexes thereof).

Formal
- Structured (Structured) - Standard, Transaction, Aggregate, etc.
- Semi-Structured (Semi-Structured) - HTML, XML, GIS, etc.
Semi-Formal
- Unstructured (Unstructured) - Video, Image, Sound, Sentence, etc.
The need for Data Quality Management of Open Government Data
Open Government Data held by public institutions has recently been recognized as an important resource for advancing national informatization, such as discovering and providing various information services through private disclosure, so it must be utilized smoothly through data quality management.
Open Government Data quality management
“Data Quality” can be defined as “a level that can provide useful value to users by securing the up-to-dateness, accuracy, and interconnection of data.” Systematic management and activities are required to continuously maintain or improve this data quality from the user's point of view. Therefore, “Data Quality Management” means “a series of activities such as setting quality goals to ensure the quality of data, diagnosing and improving quality, and related tools to support them” to provide useful value to users.
In general, data quality management has been recognized as a work performed in the operation and reuse stage after data construction, but looking at the results of the government-wide quality diagnosis project of public institutions, the cause of major quality issues, including the operation and reuse stage of data. The cause can also be found in the absence of data quality management activities at the stage of information system construction. When public institutions perform data quality management activities, data quality management is systematized to secure a system that is applied throughout all stages in consideration of the information life cycle from data construction to operation and reuse as shown in the data quality management concept diagram below. Should be.
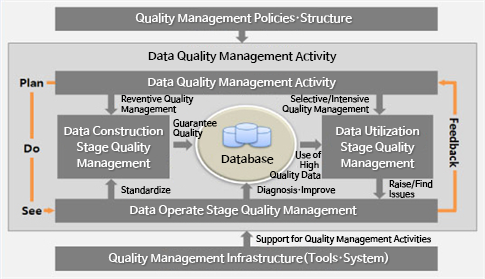
Manuals and guidelines related to data Quality Management
Instroduction of standards for OGD
Overview ofstandards for OGD
In order to facilitate the provision and reuse of open government data, we define common open standards to apply when opening government data, publication standards for each dataset field (provided items, attribute information, provision format, etc.) and other data open standards.
Applicable target : administrative and public institutions
Data Catalog of the standardized OGD (120 datasets as of 2020)
- Parking information
- Basic information on building permits
- Health Promotion Center
- Animal Protection Center Information
- City Park Information
- Construction license exclusive use area
- Dementia Center
- Local Food Certification Information
- Child protection zone
- Construction permit site location
- Camping (camping) ground
- City Tour Information
- Public toilet
- Building permit type
- Tourist information
- Road sign
- Social enterprise
- State of major commercial districts nationwide
- Fishing site information
- Road safety sign
- Unmanned Civil Application Issuance Information
- Agricultural and livestock products wholesale market meridian price
- Garosu-gil Information
- Speed bump
- traditional market
- Agricultural, livestock and livestock and livestock survey prices
- Local cultural relics
- Bridge
- Cultural Festival
- Mountain information
- Bid announcement
- Bus lane information
- B&B/Pension Business
- Trails
- Contract information
- Traffic Light
- Performance event information
- Areas with frequent traffic accidents
- Successful bid information
- One-way road
- Free Food Service
- Urban railroad route information
- Individually announced land price information
- Unmanned traffic enforcement camera
- CCTV
- Urban railway history information
- Individual house price information
- crosswalk
- Day care Center
- Urban railway operation information
- Elementary and secondary school locations
- Pedestrian priority road
- library
- bicycle storage
- Elementary school commuting area
- Sleepy shelter
- Lifelong Learning Course
- Bicycle rental
- Middle school school group
- Automobile maintenance company
- Recreation forest
- Security information
- High school school group
- 109 Smart Street Light
- Tourist information center
- Road tourism information
- High school criticism zone
- Safety emergency bell location
- Rural Experience Recreation Village
- Local special distance
- Education administrative area
- Transportation Support Center Information
- Water quality inspection
- Museum and Art Gallery information
- Information related to school districts
- Food truck permission zone
- Electric vehicle charging station
- Drinking water communal facility (spring water)
- Pedestrian road
- Child welfare meal information
- Free WiFi
- Agricultural machinery rental information
- Overpass information
- Senior preferential treatment designated business
- Public facility opening information
- Village company
- Road tunnel information
- Protected areas for the elderly and the disabled
- Non-smoking area
- Forest fire risk area
- Rest area information
- Electric wheelchair quick charger
- Car wash
- Civil defense evacuation facilities
- Car rental company information
- Female safe courier service
- Guardian
- Automatic Heart Shock Machine
- Ground subsidence information
- Female security guardian house
- Hot shelter
- Small public facilities risk designation information
- Earthquake and tsunami shelter
- Fire vehicle exclusive zone
- Disaster risk zone
- Resident priority parking information
- Household waste information
- Fire-fighting water facilities
- Legal area (eup, myeon-dong) information
- Towing vehicle storage
- Food waste payment certificate price information
- Variable electronic sign
- Continuous cadastral figure information
- Automobile inspection office
- Pay as you go bag price
- Public transport transfer center
- GIS building integrated information
- Recycling Center
- Wildlife Rescue Center Information
- Parking prohibited (designated) areas
- earthquake outdoor shelter
- Temporary Residential Facility for Earthquake-Current Use
Standards for Data Quality Management
Data Common Standard Guide
Due to the lack of unified terminology for business-related information, there is no effective way to determine whether or not the DB is redundant, so it is necessary to support a standard terminology system that can be used in common for the shared use of information between similar businesses.
For the noun-type vocabulary used in business at each level of administrative agency, an administrative standard terminology dictionary is provided so that it can be used when building and operating an administrative information database system.
By clarifying the boundaries of the meaning of the terms, the same terms can be used for terms with the same meaning, so that communication between organizations can be facilitated.
It provides the basis for assigning the same physical data element name to the logical data element name.
The use of heterophonic synonyms can be excluded by providing standard terms for synonym groups.
Introduction of guidelines for standardization of databases of public institutions
Summary
Introduction of guidelines for standardization of databases of public institutions Summary
| Last revised date | March 20, 2019 (Notification No. 2019-20 of the Ministry of the Interior and Safety) |
|---|---|
| Supervisory Agency | Open Government Data Policy Division, Government Innovation Organization Office, Ministry of the Interior and Safety |
| Target institutions | Central/local governments, public institutions pursuant to Article 3, No. 10 of the National Informatization Act |
| Main contents | Establishment purpose and scope of application, standardization management by each stage of construction and operation, common standard terminology, metadata, inspection and action, etc. |
The need for standardization guidelines for public institutions
Summary
Article 23 (Standardization of Open Government Data) of the ACT ON PROMOTION OF THE PROVISION AND USE OF PUBLIC DATA (Open Government Data Act) Open Government Data in order to lay the foundation for high-quality data reuse by defining a standardization system to be observed at each stage of creation, operation, and release of public institution databases. In accordance with Article 50 (Standardization) and Article 59 (Standardization) of the Enforcement Decree of the e-Government Act, the 「Guidelines for Standardizing Databases for Public Organizations」 has been established.
※ The “Guidelines for Standardization of Administrative Information Database” enacted in 2008 (notified by the Ministry of Government Administration and Home Affairs) has been abolished and replaced with this guideline.
Contents of public institutions' database standardization guidelines
-
Metadata registration and current management using the institutional meta-management system for systematic management, integration and linkage of databases owned by public institutions
※ Metadata, institutional metadata management system definition (Article 2), metadata management (Chapter 3) -
Specify the specific scope and role of work for performing public database standardization activities
※ Institutional standardization general (practice manager) and individual information system manager (task manager) are divided into roles (Article 5) -
Standardization of public database standards and presentation of measures
※ Activities to check the standardization level by referring to the Open Government Data quality management level evaluation index (Article 13) -
Specific step-by-step measures for standardization of public databases when performing informatization projects
※ Segmentation of outputs and scope of work to be managed when ordering, executing, and supervising informatization projects -
Simplify procedures such as standard term management and specify the time limit for corrective action (3 months)
※ Simplification of procedures such as establishment and amendment of common standard terms (Articles 16 and 17), and setting deadlines for action requests for correction during regular inspections (Article 19)
Download guidelines for standardizing public institutions' databases
Purpose and basis for implementation
Purpose and Promotion Guide
The quality management activities at the institutional level are evaluated to ensure the appropriate quality level of Open Government Data generated, acquired and managed by public institutions,
and the establishment of a Open Government Data quality management system within the public sector and the creation,
opening and Usage of high-quality Open Government Data
Article 22 (Standard Management of Open Government Data) and Article 17 (Quality Diagnosis and Improvement of Open Government Data) of the 「Open Government Data Provision and Usage Act」
Evaluation System
Evaluation Guide
Evaluation items 9 evaluation indicators in 3 areas (institutions, DB, data quality management)
- Institutional quality management: Evaluation of institutional quality base, capacity building, standardization system, etc.
- DB quality management: To perform the agency's own business
Owned database (DB) created, acquired and operated
evaluation - Data quality management: Evaluation of error rate of data stored in DB and open data in Open Government Data portal
Institutional quality management (30 points), DB quality management (45 points), data
Sum of scores for each area of data quality management (25 points)
20 years of Open Government Data provision and operation status evaluation (35%) and reflection in government innovation evaluation
Evaluation Structure
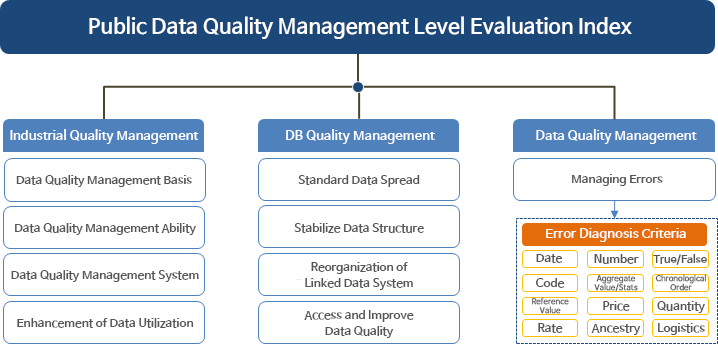
Evaluating the level of OGD quality management
- plan - Data Quality Management Basis, Data Quality Management Ability, Data Quality Management System
- build - Standard Data Spread, Stabilize Data Structure, Reorganization of linked data system
- operation - Assess and Improve Data Quality, Managing Errors (Error Diagnosis Criteria : Date,Number,True/False,Code,Aggregate Value/Stats,Chronological order,Reference value,price,quantity,Rate,Ancestry, logistics)
- reuse - Enhancement of Data Reuse
Detailed information on evaluation grade(s)
Introduction of guidelines for standardization of databases of public institutions Summary
Detailed information on evaluation grade(s)
| Level 1(optimization) | A virtuous cycle system of data quality management activities for the entire organization is established, and quality improvement and maintenance of Open Government Data are guaranteed through this |
|---|---|
| Level 2(Systematization) | The level at which the data quality management process at the organizational level is implemented and the systematic performance of data quality management activities is possible. |
| Level 3(Management) | The level of data quality improvement is possible through management and control of essential activities for data quality management. |
| Level 4(Introduction) | The level at which data quality management is recognized and basic quality management activities such as quality diagnosis are introduced and started. |
| Level 5(Pre-introduction) | The level of performing basic quality management activities or performing only partial quality management activities due to insufficient recognition of data quality management. |
Evaluation target
Information on the Evaluation Target
- All public sector organizations that fall under Article 2 (Definition) No. 1 of the Open Government Data Act are subject to evaluation (except for the National Assembly, Court, Constitutional Court, Central Election Commission, Supreme Prosecutors' Office, and National Human Rights Commission)
- In 2019, only central administrative agencies (43) and local governments (17 cities/provinces, 226 cities/guns/gu) will be implemented, and public institutions will be implemented from 2020.
- Central government and their bodies: There are 43 target agencies pursuant to the 「Government Affairs Evaluation Act」, and affiliated agencies are evaluated by being included in the upper level agencies.
- Local authorities: Evaluate 17 regional governments and 226 basic governments under the Government Affairs Assessment Act.
- Public institutions: Public institutions under the 「Act on the Operation of Public Institutions」, local corporations and local corporations under the 「Local Public Enterprise Act」, special corporations established under special laws, etc.

Evaluation Index
| Area | Evaluation Index | Pointed | Evaluatory Contents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agency | Data Quality Management Basis | 5 | Establishing a data quality management plan at the institutional level, carrying out planning tasks and checking the results of actions, etc. |
| Data Quality Management Ability |
5 | Inspection of data quality management training and communication activities (business consultation) to reinforce the quality management competency of the person in charge of the institution | |
| Data Quality Management System |
10 | Check the definition of data standards at the institutional level, and efforts to apply and spread government standards within the institution. | |
| Enhancement of Data Reuse |
10 | Define consumer requirements processing standards, comply with processing procedures, analyze consumer requirements and check improvement efforts | |
| DB | Standard Data Spread | 15 | Institutional data standards are reflected in the diagnostic database standard, and the application rate is checked whether the standard of the diagnostic database defined in various definitions has been applied to the columns in the central meta system. |
| Stabilize Data Structure | 15 | Defining essential outputs of the diagnostic DB structure, comparing the defined output information (tables, columns) and information in the central meta system to check the matching rate, etc. | |
| Reorganization of linked data system |
5 | Linked data management information definition, link quality check and improvement, communication system between internal and external organizations, etc. | |
| Assess and Improve Data Quality |
10 | Quality diagnosis target and diagnosis criteria definition, quality diagnosis using diagnosis criteria, error data discovery, error data improvement task action results, etc.checked ) | |
| DATA | Managing Errors | 25 | Check the DB and file-based datasets error rate to be diagnosed |
Evaluation area for each institution (evaluated according to the size of the institution, business characteristics and DB type)
- Central administrative agencies, local governments (provinces), public enterprises, and fund management are evaluated in all areas (9 indicators)
- Local governments (Si/gun/gu), consigned public institutions, and metropolitan public corporations and industrial complexes evaluate only the data quality management area (1 indicator)
| Area | Evaluation Index | Central government and their bodies, city and/or municipal level, publicly owned company and fund management type | Si, Gun-gu, consignment execution type and wide area construction·industrial complex | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Management | DB Department | General Management | DB Department | ||
| Industrial Quality Management |
Data Quality Management Basis |
O | |||
| Data Quality Management Ability |
O | ||||
| Data Quality Management System |
O | ||||
| Enhancement of Data Reuse |
O | ||||
| DB Quality Management |
Standard Data Spread | O | |||
| Stabilize Data Structure | O | ||||
| Reorganization of linked data system |
O | ||||
| Assess and Improve Data Quality |
O | ||||
| Data Quality Management |
Managing Errors | O | O | ||
Data Quality Management Education Guide
Support for strengthening institution-centered data quality management capabilities such as expansion of practical training such as quality diagnosis and discovery of business rules, professional training courses (basic and in-depth training, etc.), opening of a permanent training center
Basic Data Quality Management (Theory) : 3H
Understanding of quality management method, level evaluation index, etc.
Basic quality diagnosis (practice) : 3H
Understanding quality diagnosis, how to use diagnostic tools, etc.
Data Quality management/diagnosis practice (theory and practice) : 4H
Data Quality management methods and procedures, business rules such as data quality management cases, profiling practice, quality diagnosis items and error improvement, etc.
Professional data quality management (theory and practice) : 18H
Data Quality management system, data normalization, SQL reuse profiling, business rule deduction, error improvement, etc.